Designed by Reed Marquardt
The controller is located at the back center of the vehicle. To balance the weight of the controller, the battery is located towards the front of the vehicle. The two motors are attached to the bottoms of the two wings.
Designed by Paul Bowman
This design is based of of the basic principles of planes having their means of propulsion extended to the sides of the center of mass. There are wings positioned at the back of the vehicle, with a motor placed on each wing. The battery is positioned just below them for easy access. The Arduino controller is placed in the front two inches back from the magnet and clear of all metal components. An aerodynamic hood will be placed over the front of the vehicle to help reduce drag.
Designed by Kartik Vaidya
The wings on the back are angled while the wings in front are flat. This is so the vehicle has enough lift when going up the incline and enough speed when going from district to district. The propellers are situated on the back wings. The battery and the Arduino controller are placed in the middle for balance.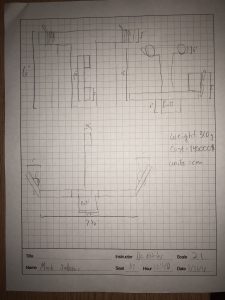
Designed by Mark Jabour
This design focuses on reducing weight by having a smaller body. The motors are positioned on an incline from the main body. The Arduino controller is placed on the top, with the battery on the bottom, and the motors at the very back of the vehicle.
Designed by Team I
This sketch shows the team’s agreed-upon design, taking elements from every design. The motors are placed on flat surfaces, as opposed to being on sloped surfaces. This should put the thrust vectors in-line with the center of gravity, allowing for greater stability. The T-shaped design allows for the necessary components, battery, Arduino controller, motors, etc. with the least weight, causing the craft to be more energy efficient.


