By: Meghan Thoreau, OSU Extension Educator
This post was published to support an immersive hands-on Environmental Summer Camp Program gears toward middle school students. The lessons focus on frog science.
Frogs are important in research. They belong to the Animal Kingdom and are used to understand biological phenomena in a variety of other animals, including how birds, mammals, and reptiles reproduce, grow and develop.
Frogs are Indicator Species
Frogs have skin that is permeable, which means things can pass through it. This allows them to both breathe and drink through their skin. It also means that anything in the environment is really easy for them to absorb. If an environment is contaminated with things like pollutants their health will really be affected. They also live on both land and in the water, which exposes them to two different environments.
Thanks to their permeable skin and duel life on and off land frogs are the go-to species to figure out how an ecosystem is doing. Scientists often look at frog populations in order to figure out how healthy, or unhealthy an environment is.
Meet the Gastric-Brooding Frog
These frogs barfed up their babies—and now scientists are trying to bring them back from the dead.
Frogs are Important to the Food Chain
Throughout the lifecycle of a frog, they play an important role in the food chain as both predators and prey. This means that taking them out of the mix has a really big impact on lots of other animals.
As tadpoles, they feed on algae, which helps to keep the water clean. Once full-grown frogs feed on lots of insects, which helps to control bug populations.
When frogs aren’t busy eating things they are being eaten, serving as a tasty meal for tons of animals like fish, snakes, and birds. (1)
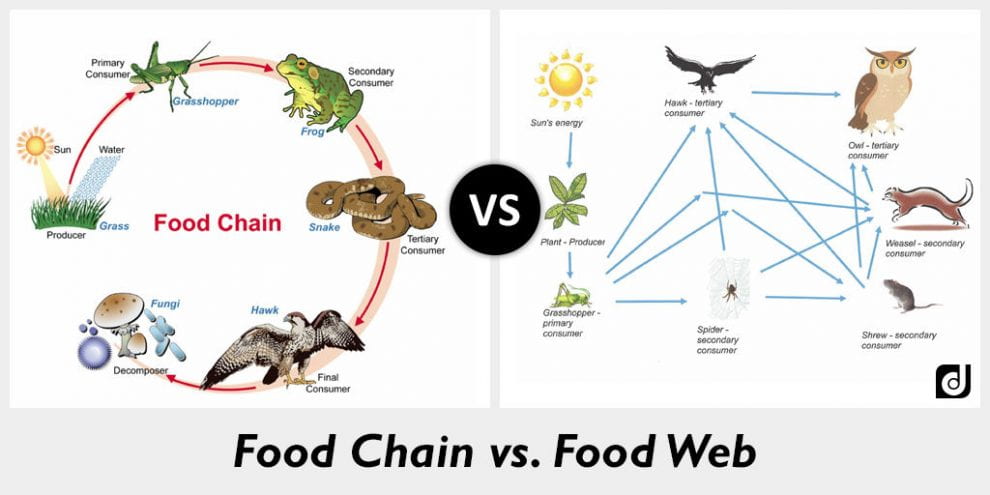
Food Chain vs. Food Web
A food chain is a linear representation or description whereas a food web is not linear and therefore includes more connections within the organisms. The two are often used interchangeably, although they are not technically the same. A food web contains multiple food chains. (2)
Career Paths
A herpetologist is a zoologist who studies reptiles and amphibians such as frogs and salamanders. Many herpetologists focus on the conservation of these species. Others use them to assess overall environmental conditions in a particular area. Read more about, How to become a Herpetrologist and consider a career in environmental science.
What Does a Herpetologist Do?
Read more, learn about the salary and required skills, What does a Herpetologist Do?
CAMP iPAD ACTIVITIES
Froggipedia
Students use iPads to access Froggipedia. Froggipedia is an engaging, interactive, powerful constructive learning Apple AR that helps students explore and discover the unique life cycle and intricate anatomical details of a frog. The app provides an immersive and engaging experience that elaborates on each phase of the life cycle of a little amphibian called the Anura. (Anura is the scientific name of the frog.)
Froggipedia helps us to observe the life cycle of a frog, such as how it turns from a single-celled egg in water to a tadpole which in turn metamorphoses into a froglet and eventually a full-grown frog. We can further dissect and observe the complex structure of its various organ systems right on our iOS devices using an Apple pencil or your finger. Thus we get the best of both worlds as we get to successfully observe and learn about the structure of a frog and yet cause no harm to life. A fun quiz, in the end, helps in absorbing the knowledge gained through this innovative app.
Wordwall Challenges
Let’s start off with some lifecycle art. Study the frog’s lifecycle below and then students can draw their own frog lifecycle in the first Wordwall challenge.
Challenge 1: Sketch the Frog Lifecycle
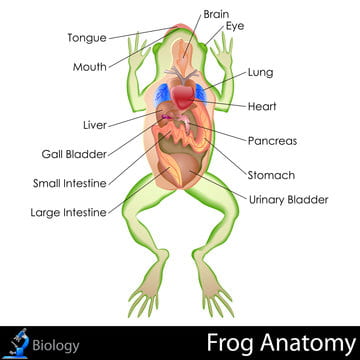
Challenge 2: Label the Missing Frog’s Anatomy
This challenge is best done after students engage in Froggipedia’s immersive AR dissection activity, which allows students to become familiar with the frog’s basic anatomy.
Challenge 3: About the Frog