Disease process:
Highleyman, L. (n.d.). Hepatitis C: The Changing Picture. Retrieved from http://www.thebodypro.com/content/art53550.html
- The Hepatitis C virus is spread when blood from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person. Most people get infected by sharing needles or other injectable drug equipment.
- Hepatitis C starts out as acute, which describes the first several months after initial contact with the virus. Acute Hepatitis C can range from being without symptoms, to a condition that needs hospitalization.
- A lot of people who have Hepatitis C don’t know they have the virus because they don’t present any symptoms at all.
- Because this is a viral infection, treatment can only help with symptoms while the immune system fights off the virus. Antibiotics don’t work for viral infections, but there are antiviral medications available.
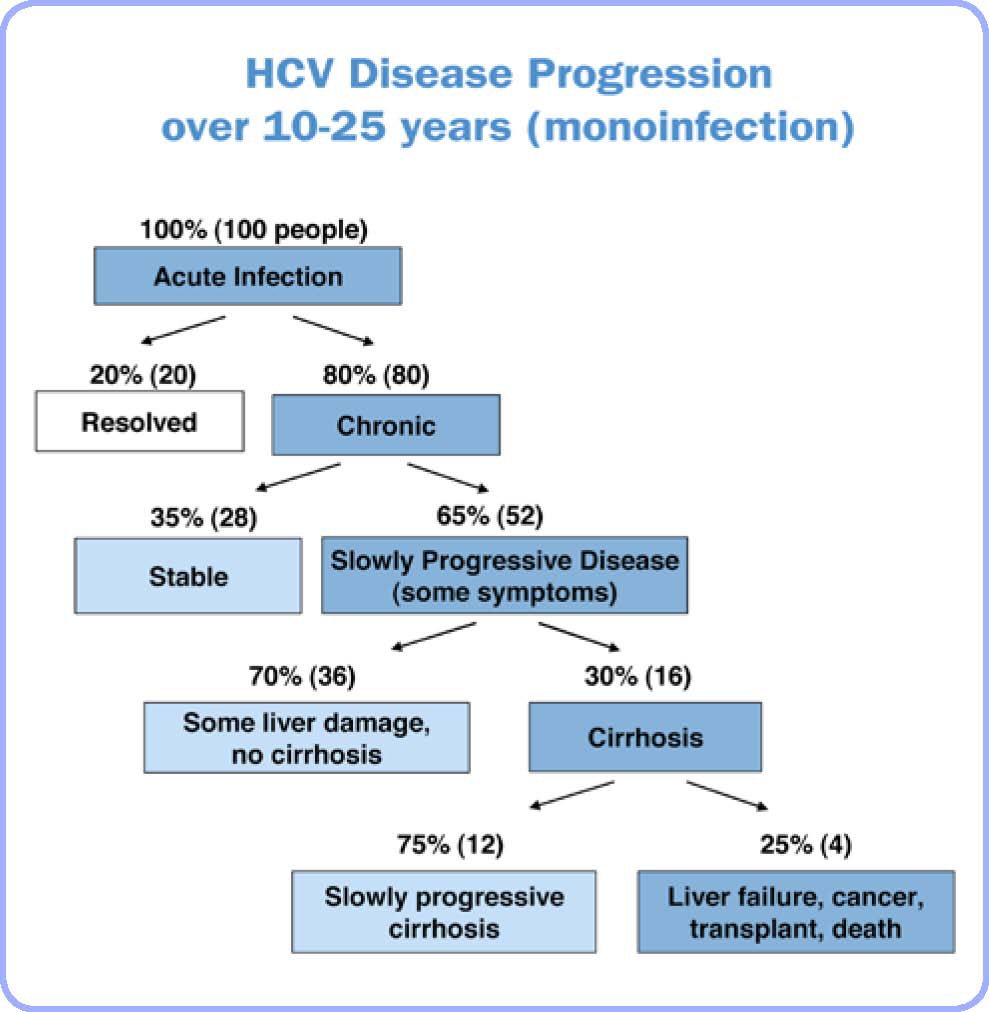
- 20% of people are able to get rid of the virus without treatment in the first 6 months, but unfortunately 80% go on to develop chronic Hepatitis C. Chronic Hepatitis C can eventually go on to cause health problems such as liver disease, liver cancer, and liver failure (McCance & Huether, 2019).
Normal vs. abnormal physiology of body sys:
Hepatitis C is an inflammatory infection of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that filters blood, fights infection, and processes nutrients. Hepatitis acts to damage this function by inflaming the liver (McCance & Huether, 2019).