What Is It? | Facts in Depth | For the Professional Diagnostician
Tomato Diseases | Bacterial Leaf Spot Fact Sheets
Bacterial Leaf Spot of Tomato
Symptoms
Foliar symptoms of bacterial spot and speck are identical therefore fruit symptoms should be used to distinguish between the two diseases. If fruit are not provided with the sample additional diagnostic tests should be conducted to confirm the pathogen causing the disease.
Stem:
- No vascular discoloration will be observed when the stems are split open lengthwise.



Images of Bacterial Leaf Spot on tomato plants.
Fruit:
- Small, greasy water-soaked spots on green fruit that become slightly raised and enlarged (1/4 inch)
- Older spots are irregular in shape, light brown to black, slightly sunken and have a scabby surface texture



Images of Bacterial Leaf Spot on tomato fruit.
Signs
Bacterial streaming from the margin of a leaf, stem or fruit lesion.



Often Confused With
- Bacterial Canker – Although bacterial spot fruit lesions may have white halos similar to “bird’s eye” spotting seen with bacterial canker, the white halo disappears as the fruit matures.
- Bacterial Speck – Look for small black pin-point lesions on the fruit with no white halo as indicators of bacterial speck. Bacterial speck lesions on fruit are superficial and can be easily scraped off of the fruit surface.
Isolation Media
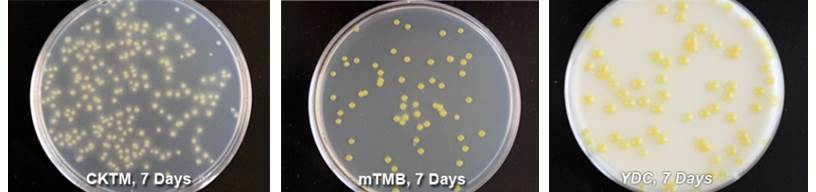
CKTM medium (pdf) is a semi-selective medium. Xanthomonas spp. colonies on CKTM plates are light yellow. Halos with tan to white colored crystals can be observed around each colony after 7-10 days at 82 °F. Colonies are round, entire and raised.
Modified Tween Medium B (mTMB) (pdf) is a semi-selective medium. Colonies of Xanthomonas spp. on mTMB plates are yellow, slightly mucoid, round, entire and raised. Colonies on densely populated plates will form a crystalized halo after 7-10 days at 82 °F.
Yeast extract-dextrose-calcium carbonate (YDC) medium (pdf) is a non-selective media used for subculturing suspected xanthomonads and clavibacters. Xanthomonas spp. colonies on YDC medium are yellow, mucoid, round, entire and raised after 3 days at 82 °F.
Available Rapid Diagnostic Tests
Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assays
- primers RST65-2/69 (Xanthomonas spp.-specific) RST primers (pdf), RST65-2 primers (pdf) (pdf)
- primers Xeu2.4/2.5 (X. euvesicatoria-specific) Xeu primers (pdf)
- primers BS-XeF/R (X. euvesicatoria-specific)
- primers BS-XvF/R (X. vesicatoria-specific)
- primers BS-XpF/R (X. perforans-specific)
- primers BS-XgF/R (X. gardneri-specific) Xanthomonas multiplex PCR primers (pdf), BS primers (pdf)
