You’ve likely seen the term “ED” pop up in conversations, health ads, or men’s wellness discussions. But what does it really mean? If you’re wondering about ED and how it impacts you or a loved one, you’re not alone. Let’s dive into what ED is, why it happens, and how it can be treated.
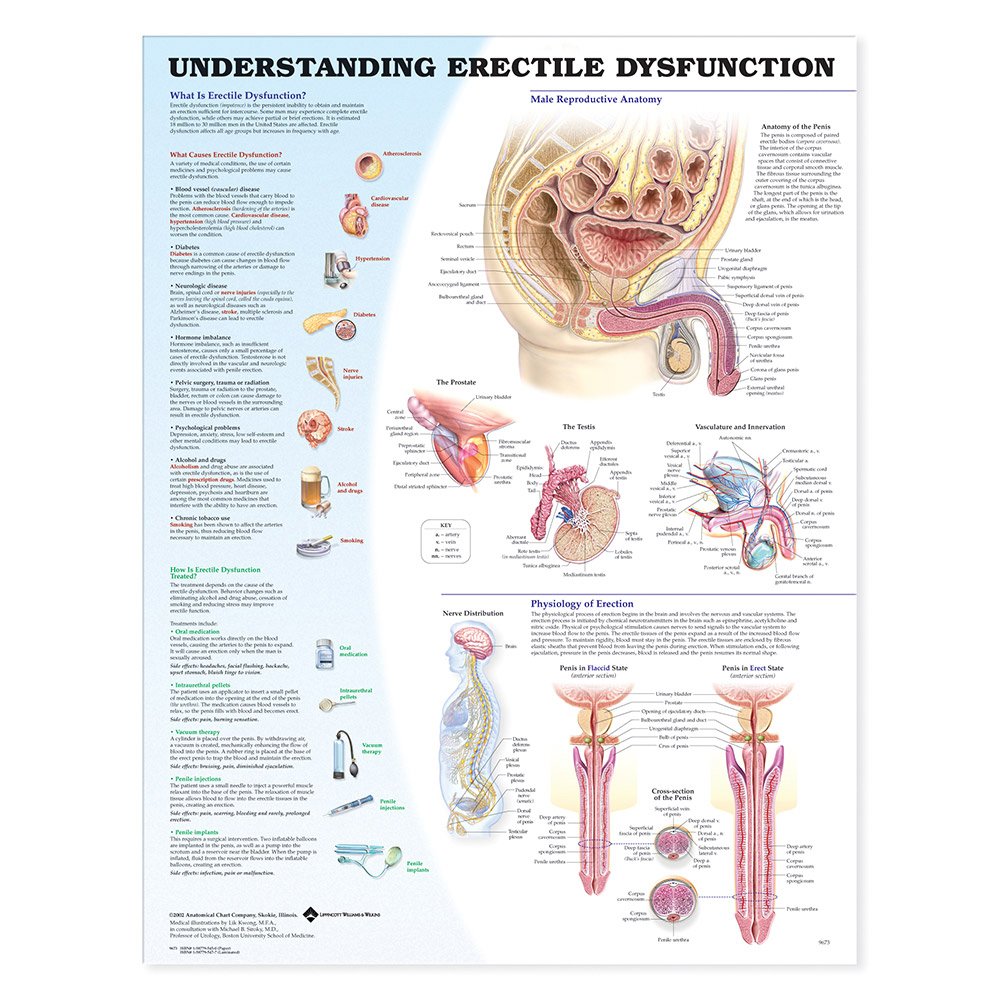
What Is ED? The Basics
ED stands for erectile dysfunction, a condition where a man is unable to achieve or maintain an erection that’s firm enough for satisfying sexual activity. This can happen from time to time, but when it becomes frequent, it can affect your quality of life and relationships.
An erection occurs when blood flows into the penis, causing it to become rigid and enlarged. This happens in response to sexual arousal, where the brain sends signals to nerves in the penis, prompting blood vessels to dilate, allowing more blood to enter. Meanwhile, veins that carry blood away constrict, trapping the blood inside. It’s this delicate balance of blood flow that results in an erection.
But when this system doesn’t work as it should, ED can occur. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty getting an erection
- Trouble maintaining an erection during sex
- Reduced interest in sexual activity
While ED is common, especially as men age, it can affect men of all ages. It doesn’t necessarily signal something serious, but it’s always a good idea to check in with a healthcare professional if it becomes a frequent issue.
What Causes ED? The Surprising Range of Factors
ED doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all cause. It can be the result of a mix of physical and psychological factors, sometimes in combination.
Physical Causes of ED
- Heart Disease: If arteries are clogged and blood flow is reduced, it can affect the ability to get or keep an erection.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves, both of which are crucial for maintaining healthy blood flow to the penis.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Low testosterone, the main male hormone, can directly impact both sexual desire and erectile function.
- Obesity: Carrying extra weight can increase the risk of ED through inflammation, poor circulation, and hormone changes.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage blood vessels, limiting the blood flow necessary for an erection.
- Medications: Some medications, including those for high blood pressure, depression, and even allergies, can interfere with sexual function.
Psychological Causes of ED
It’s not just about the body. Your mind plays a huge role in sexual function. Stress, anxiety, depression, and even relationship problems can contribute to ED. The psychological burden of performance anxiety, for example, can make it harder to enjoy sex and can create a vicious cycle of worry and dysfunction.
Can ED Be Treated? Absolutely.
The good news is, ED is treatable, and there are several options to explore depending on the cause. It’s important to get to the root of the problem, whether it’s physical, psychological, or a mix of both.
1. Lifestyle Changes for Prevention and Management
Many men see improvements in their symptoms with simple lifestyle changes:
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and reduce stress.
- Maintain a healthy diet to keep your heart and blood vessels in good condition.
- Cut back on smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, both of which can contribute to ED.
Making these changes can go a long way in improving both overall health and sexual function. However, if lifestyle changes alone don’t cut it, there are other treatment options available.
2. Medical Treatments
- Medications: Drugs like Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra (vardenafil) are common treatments that help improve blood flow to the penis. These medications are effective for many men, but they need to be taken under a doctor’s guidance.
- Hormone Replacement: If low testosterone is contributing to your ED, hormone therapy may help.
3. Other Therapies
- Counseling: If stress, anxiety, or relationship issues are at the core of your ED, therapy can be incredibly helpful. Working through these issues with a therapist or counselor can restore not only your sexual health but also your emotional well-being.
- Vacuum Devices: These non-invasive devices use suction to draw blood into the penis, helping create an erection. They’re a good option for men who can’t or don’t want to take medications.
- Surgical Options: For men with persistent ED, surgical implants like penile prosthetics can offer a permanent solution when other treatments fail.
Your Next Step: Consult a Professional
The most important thing to remember is that you don’t have to suffer in silence. ED is treatable, and there’s no shame in seeking help. A urologist, a doctor specializing in male reproductive health, can conduct tests to determine the underlying cause and recommend the best course of action.
In fact, the sooner you address ED, the more likely you are to find a solution that works for you. Whether it’s making healthier lifestyle changes, trying medications, or seeking therapy, help is available, and you don’t need to face this alone.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can ED happen to younger men?
Yes, while ED is more common in older men, it can affect younger men as well, often due to stress, anxiety, or other psychological factors.
2. How do I know if my ED is caused by a physical or psychological issue?
A healthcare professional, especially a urologist, can help determine the cause of your ED through tests and a thorough discussion of your health and lifestyle.
3. Are there any long-term solutions for ED?
Yes, for some men, treatments like hormone replacement therapy, medications, or surgical implants can offer long-term relief. However, the best treatment depends on the root cause of your ED.
4. Can lifestyle changes help with ED?
Absolutely! Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol can improve blood flow and reduce stress, which in turn can improve ED symptoms.