What is Cloud Computing? There are several definitions. At first, Khalid and Shahbaz (2013) discuss that Cloud Computing is an exercise of digital resources, including hardware and software, which can be uploaded or downloaded through a network, especially the Internet. The name “Cloud” is derivative from a cloud-shaped notation that used on large networks in a high frequency. Cloud Computing points at “facilitating convenient network access to a shared collection of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provided and launched with the least amount of management effort or service-provider interaction” (Khalid, Shahbaz, 2013, P.348). Khalid and Shahbaz (2013) divide Cloud into public clouds, private clouds, hybrid clouds and virtual private cloud. The former three are categorized by the dimensions of the Internet servers, the quantities of customers and the security to access while the last is a special one about cryptographic cloud storage.
Additionally, Pallis (2010) comes up with the definition that Cloud Computing is an innovative domain in Internet computing that offers neoteric perspectives in internetworking technologies, proposes issues in the areas of architecture or design and implements existing networks and digital servers.
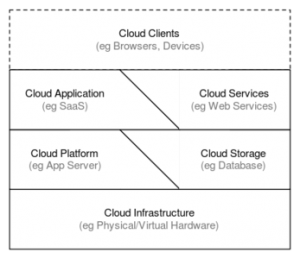
Authoritatively speaking, the NIST definition of Cloud Computing is “a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction” (Mell, Grance, 2011, P.3). From the official definition, it is obvious that the five basic characteristics of Cloud Computing are on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity and measured service. Besides characteristics, the three service models we are familiar with in normal life are software, platform and infrastructure.
As one of the earliest companies employed Cloud Computing in business, IBM offers Cloud Computing ratings. Medford (2008) declares that a rating system Resilient Cloud Validation Program was announced by IBM so that business companies can validate their properties and functions. The measure moved 200 small firms into the cloud computing service markets. Later in 2013, IBM expanded its Cloud Consulting Services Portfolio to offer customers strategy for industry and line-of-business. Taft (2013) claims that the company created “a catalog of fast-start industry offerings delivered as a service for cloud-based applications. The open systems that IBM combined Cloud Computing with business analytics to serve for customers and enterprises make this new technology become more and more popular in the business filed.
References:
1. Khalid, A., & Shahbaz, M. (2013). CLOUD COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY: SERVICE AND OPPORTUNITIES.Pakistan Journal of Science, 65(3), 348-351.
2. George Pallis (2010). Cloud Computing: The New Frontier of Internet Computing. IEEE Internet Computin, 1089-7801/10.
3. Peter Mell, Timothy Grance (2011). The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing. National Institute of Standards and Technology, 800-145.
4. Medford, C. (2008). IBM Offers Cloud Computing Ratings. Red Herring, 3.
5. Taft, D. K. (2013). IBM’s Cloud Consulting Services Portfolio Expands. Eweek, 4.