Normal Physiology
- Main function of the lungs = supply adequate oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the blood
- Air enters the body through the nose and mouth and travels done the trachea, into the smaller airways (bronchi and bronchioles), reaching the alveoli, balloon-like sacs at the end of the bronchioles.
- The alveoli are surrounded by thin capillaries that allow for the exchange of gases between the pulmonary system and the blood.
- Upon inhalation, the lungs fill with oxygen-enriched air providing oxygenation for the blood. Upon exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the lungs which has been removed from the blood through alveolar-capillary exchange.
- Adequate gas exchange occurs in the lungs when air passages are unobstructed and the Ventilation / Perfusion Ratio (V/Q) is 0.8:
- 4 liters of air enter the respiratory tract while 5 liters of blood diffuse through the capillaries every minute (McCance & Huether, 2019)

[Mads, Lause & Mogensen, Mads. (2019)]
Childhood Asthma is a disorder caused by chronic inflammation of the bronchial mucosa. It is the most prevalent chronic pediatric disease, and ½ of the total asthma cases are developed and diagnosed during childhood. Asthma is caused by a complex interaction between environment and genetic susceptibility and presents more severely in younger children due to smaller airway diameters (McCance & Huether, 2019).
Pathophysiology
- Episodic attacks caused by an IgE mediated Type I hypersensitivity immune over-response that results in reversible bronchial hyperresponsiveness, bronchoconstriction, mucosal edema, increased mucous production and airway obstruction that leads to ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch, hypoxemia and expiratory airway obstruction.
- Early Asthmatic Response – acute bronchoconstriction that peaks at 30 minutes and lasts from 1-3 hours
- Bronchial mucosa comes in contact with an antigen which activates dendritic cells in lung tissue and alveoli that present the antigen to T helper cells (CD4+ T cells) and release various inflammatory cytokines
- IL-4 activates eosinophils and B lymphocytes
- IL-5 causes activation and proliferation of eosinophils what can result in direct tissue injury, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, epithelial damage and formation of scarring of the airway
- IL-8 activates neutrophils that invoke a hyper reactive immune response
- IL-9 promotes mast cell proliferation
- IL-13 results in decreased mucociliary function and causes bronchoconstriction and airway remodeling
- IL-25 Increases occurrence of airway remodeling
- Inflammatory mediators activate inflammatory cells and cause vasodilation, edema, bronchospasms, mucous secretion and increased capillary permeability (McCance & Huether, 2019)
- Bronchial mucosa comes in contact with an antigen which activates dendritic cells in lung tissue and alveoli that present the antigen to T helper cells (CD4+ T cells) and release various inflammatory cytokines
- Late Asthmatic Response – begins 4-8 hours after early response and is characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness
- Recruitment of lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils through chemotaxis causes a release of inflammatory mediators resulting in bronchospasms, excess mucous secretion and edema
- Prolonged smooth muscle contraction leads to scar tissue and collagen matrix formation which can lead to airway scarring
- Accumulation of mucous and debris caused by impaired mucociliary function form plugs in the airways that result in airway remodeling
- Mucous plugs cause air trapping and hyperinflation distal to the obstruction that can result in hypoxemia and increased work of breathing (McCance & Huether, 2019)
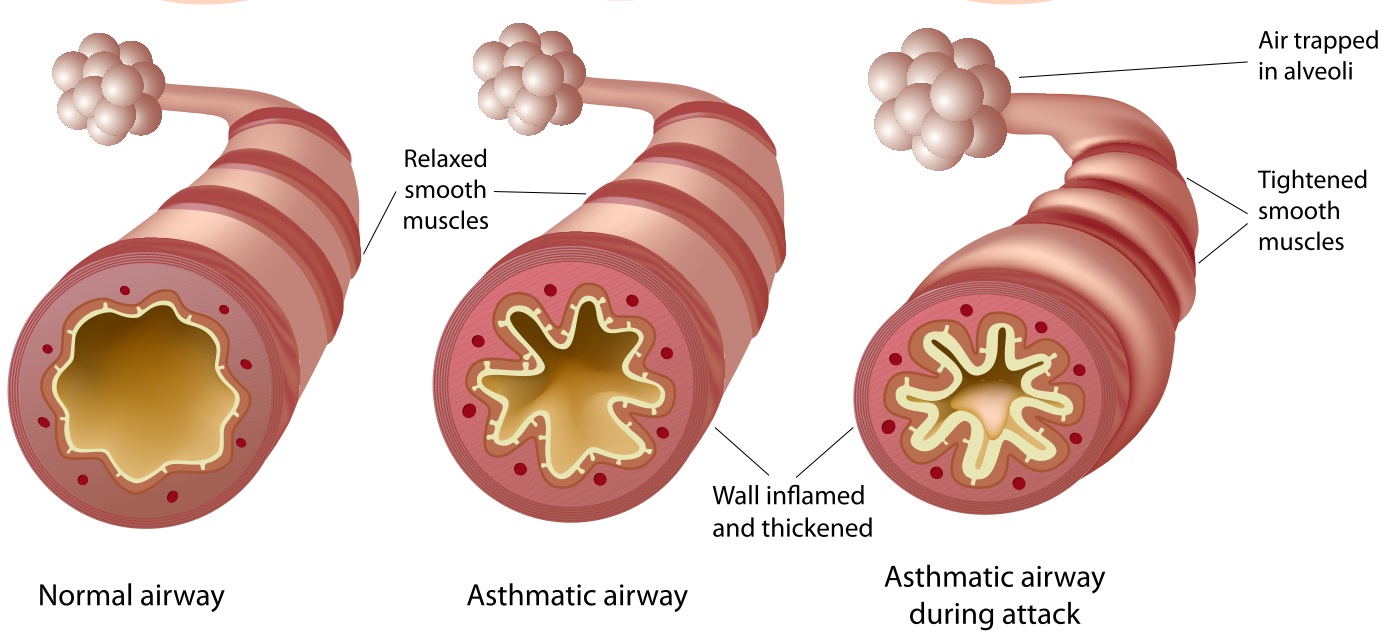
[ Simple Bio, 2019]
Manifestations of Childhood Asthma
- Asymptomatic between episodes
- Nonproductive cough
- Dyspnea
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnea
- Prolonged expiration
- Wheezing upon expiration
Diagnostic Tools / Tests
- Rule out other disorders / diseases that present similarly to asthma
- Lung function test (spirometry)
- Exhaled nitric oxide test
- Thorough medical history including family member history
- Allergy testing (Asthma Diagnosis, 2019)
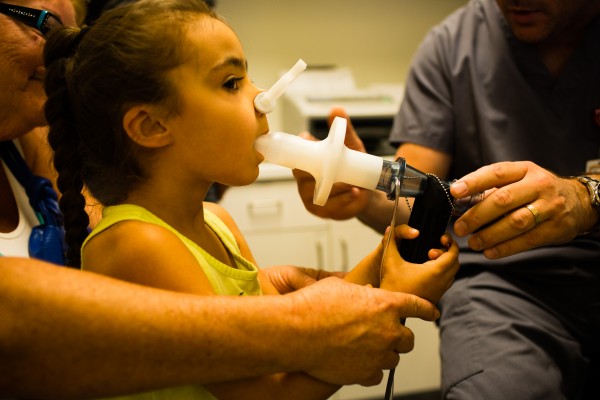
[Pulmonary Function Testing, 2019]