Note: This is an article I published about my experiences at the Paris climate conference in the newsletter for the Sierra Club Central Ohio Group (pdf).
In December I traveled to Paris as part of the Sierra Club delegation to the COP 21 climate conference. The conference marked a turning point for humanity, resulting in an agreement by almost 200 countries signaling that the age of fossil fuels is over.
Although I did not have a badge for the actual climate negotiations – the United Nations issued many fewer badges than usual this year – Sierra Club members got daily reports from Fred Heutte, lead volunteer for the Federal and International Climate Campaign.
That left most of us free to attend civil society events and actions – and there were a lot. Throughout the two weeks, the Sierra Club had a booth at Climate Generations, the space next to the negotiations where hundreds of organizations had displays, and as many as eight speakers and panels on climate were going on simultaneously.
There were also dozens of meetings, festivals, actions, and other events occurring daily throughout Paris – sometimes it was hard just hearing about them all. There was no way to attend everything – you had to choose. But no matter what you picked, it would be good.
The hostel where I stayed, called Place to B, had daily programs featuring speakers such as James Hansen, Vandana Shiva, and Amy Goodman. There were also numerous side conferences such as UNESCO’s Earth to Paris, featuring an all-star lineup of scientists and activists and an interview with Secretary of State John Kerry; and the Climate Summit for Local Leaders, at which 1,000 mayors pledged to take their cities 100 percent renewable by 2050.
Here are some highlights from my time in Paris:
1.5 degrees. Although most observers expected participating countries to agree to limit warming to 2°C, almost no one anticipated the momentum to lower that limit to 1.5°C. It started with a call from climate vulnerable countries led by the Marshall Islands. Then France and Germany joined, then Canada and Australia, then the United States and China.
In the end, all countries pledged to limit warming to “well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels” and “pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C, recognizing that this would significantly reduce the risks and impacts of climate change.”
Indigenous peoples. Indigenous people from around the world were key players in many events such as an anti-fracking summit and a conference on women at the frontlines of climate change.
They also led the Indigenous Flotilla, featuring the Canoe of Life which traveled from the Amazon. Dozens of indigenous people canoed and kayaked into Bassin de la Villette to present world governments with their “Living Forest” proposal drawing from indigenous experience to live in harmony with nature.
Rights of nature. A two-day International Rights of Nature Tribunal explored the rights of nature as a legal concept and how they might be defended in a series of cases against violators of those rights. Cases included:
- Climate crimes against nature such as fossil fuels, deforestation, and water use;
- Financialization of nature, including carbon trading and REDD;
- Agribusiness and GMOs;
- Criminalization of environmental activism and murders of activists;
- Shale fracking operations, which speakers argued was akin to rape of the earth;
- Megadams in Brazil that destroy ecosystems and displace indigenous people;
- Ecocide through oil operations in Ecuador’s Yasuni National Park.
Trade and climate. Throughout the two weeks were events on trade, unions, jobs, and climate, emphasizing that while addressing climate change through renewable energy creates jobs, bad trade deals destroy both jobs and climate. The culmination was a general assembly at the Climate Action Zone on “Capitalism and Climate” featuring Naomi Klein.
While climate agreements are not legally binding, Klein said, trade deals such as NAFTA and the TPP are not only binding but would allow corporations to sue to overturn laws protecting the climate that hurt their profits. The trade and climate movements should work together to defeat this, she said.
Exxon trials. There were two mock trials of Exxon similar to the successful RICO case against tobacco corporations by the Justice Department. A recent investigation by Inside Climate News shows that Exxon was conducting some of the foremost climate science in the 1970s and 80s, but in the 1990s chose to bury this information and instead fund climate denial campaigns.
In the first trial, held at the People’s Climate Summit, Bill McKibben and Naomi Klein called a series of witnesses affected by climate change to show the damage that Exxon’s denial campaigns have done. The second event featured Matt Pawa, an environmental attorney who has won cases against Exxon and AEP, building a RICO case based on recently released documents.
On and off police actions. Before COP 21 started, French authorities banned large climate marches due to the November 13 terrorist attacks in Paris. The attacks were still fresh when I arrived. Massive numbers of flowers, candles, photos, and other mementos were placed around the statue of Marianne at Place de la Republique as well as in front of and across several blocks near the Bataclan club, where most of the victims lost their lives.
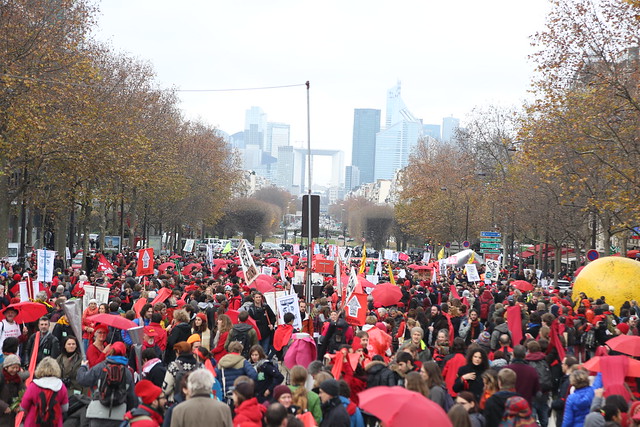
I was taking photos at Place de la Republique on November 29 when police cracked down on a few hundred demonstrators, and I was nearly swept up. By December 12, thousands of activists were flooding the streets, and French authorities finally relented and gave them a permit. The result was a beautiful Red Lines demonstration organized by 350.org.
The climate conference in Paris was historic, not only for the agreement it produced, but for the breadth, depth, and global nature of events and actions surrounding it. I feel privileged to have participated in these events and witnessed history being made.