By Danielle Latman
Ohio State MBA student
Wednesday, 5:30pm: Rain pelted the windows as I sat in the back of the van with seven men, interviewing a young woman about administering health information in the Gondar region.
We were pulled over on the side of the road on the outskirts of Gondar city, asking the woman about her role as a Health Extension Worker (HEW). This 8-year-old program trains and employs women to provide basic health education, information and supplies to each kebele (small municipality) throughout Ethiopia. The HEW program responds to the limited formal health care in the country, with very few doctors and nurses to meet the population’s needs.
We were meeting with the woman, whose name translates to “Love,” to learn more about the role of HEW and if/how they could be helpful to the rabies plan.
We (Danny, Javed, Niraj and myself, plus our three guides/translators from the University of Gondar, and our driver Amhara) were sitting in the van because of the rain outside, and because the HEW’s post was far away.
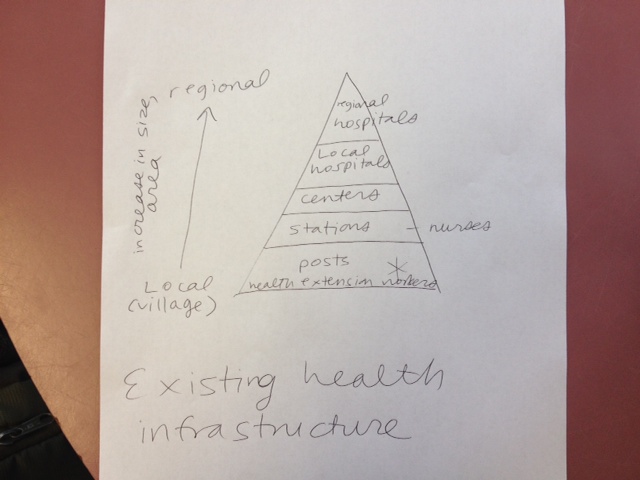
Surprisingly, this wasn’t our first van interview of the day. We started the afternoon by visiting the health station near Gondar city. The Ethiopian health system has a set structure operating from the kebele to the regional level.
The HEW operate from a local kebele post and visit families door-to-door. Above them is a health station, with nurses. Above that is a health center. And the highest level of care is provided at the hospital level, but only two main hospitals (in Addis and Gondar) can provide a wide range of health services.
At the health station we could meet with a HEW coordinator. Our van idled for a few minutes in front of the short cement building while the team members discussed with our hosts what we wanted to ask. A young woman approached our van to ask what we wanted. Our hosts spoke with her in Amharic, and then the young woman left and shortly returned carrying an umbrella over the head of another woman, wearing a white coat.
Sister Abanesh entered the van, sat in front and answered some of our questions about Ethiopia’s 17 health priorities which the HEW workers focus on. She was the coordinator and managed six HEW. But we didn’t get to talk to her long, since the director of this health center preferred that we speak with him formally in his office.
So we got out and walked to his office in the health station compound. On the walk we saw some cool posters promoting different positive health behaviors, which Danny and I (the marketing team) were very interested in for our part of the project.
We filed into the director’s office, sitting in chairs around his desk. He answered our questions about the training and reporting processes for HEW, and Sister Abanesh gave us some pamphlets that they use for family health education.
One important thing we have learned is that, while there is an overall 40 percent literacy rate in Ethiopia, almost all households have at least one child who can read, and so the child will read information for the whole family, leading to an almost 100% literacy rate at the household level. Then they showed us the storage area where they keep the vaccines cold.
We left with smiles, thank you’s and handshakes all around, then drove to our second van meeting of the day.
It is worth noting that the health station is located in a Jewish area just outside Gondar. We saw a house with a wooden Jewish star outside painted blue and white.
Our first meeting of the day had been no less surprising. We met with a group of faith healers who were having their association meeting at 9am. We all gathered behind their shack in downtown Gondar, which had posters for remedies like aloe vera curing HIV.
We had heard that a lot of people in Ethiopia use traditional or faith healing (bahawali hakeem in Amharic) instead of or in addition to modern medicine, especially the rural population. About 90 percent of Ethiopians live in rural areas. Thankfully, our university guides Akilew and Debasu had contacts with them and were able to set up a meeting.
Though we directed our questions to the group of about seven men and one woman faith healers, for the most part only the chairman responded. We asked about their motivation for becoming faith healers. For some it was a change from their strict religious backgrounds. For others it was passed down in their family. We also asked if they had or would ever collaborate with doctors or other medical scientists in their treatment. We were pleasantly surprised to learn that they are open to collaborations, especially with treating dogs that have rabies.
We then visited a vaccine storage facility, a health clinic, and a vet clinic (with a very sad-looking chicken outside). Rabies vaccines have to be kept cold – one of the challenges in warm climates like those in Africa. The veterinarian told us they had administered 500 rabies vaccines since March and showed us their cold storage and even a sample vaccine, which came from India.
After our morning meetings, our host Tamiru suggested we go to Hotel Taye for traditional Ethiopian coffee. In the second floor lounge area, a woman was roasting coffee beans and cooking ground coffee in a traditional pot over hot coals. Rose petals were strewn in front of her cooking area.
It was a very long, insightful and rich work day which lasted about 12 hours, and some of us retired early to be well-rested for what will surely be another full, surprising and enriching day.